Introduction
First I suppose we should cover a basic definition of data science and what it involves, but keep it brief, as it’s far more engaging to start exploring than discuss what it is. For our purposes, data science is the exploration of data to gain insights that can be used to take action (hopefully that benefit the user, organization, or humanity as a whole).
There are a few basic steps in exploring data that one goes through:
- Gathering data
- Cleaning, organizing, and/or structuring data
- Applying computations to the data
- Visualizing the data
- Achieving insights or actionable data
We will cover these steps in more detail in future writings, for now we need to get set up with the tools we will need to effectively perform these steps. Most data science is done using some form of programming, and two of the more popular languages used for data science are Python and R. Dont worry about choosing a language just yet and don’t worry if you know nothing about programming, that should not intimidate you, its no different than any other skill you’ve learned.
There are no shortage of tools or platforms that can be used for data science, since we are focused on the construction industry we are going to work primarily with three platforms: Python, R, and Excel. Now when it comes to Microsoft’s Excel we are not going to cover that here, it is assumed that if you have it, it is already up and running on your computer.
This first part will focus on downloading and installing some of the required tools, part II we will jump into Python and some of it’s basics, part III we will jump into R and some of it’s basics, and part IV will focus on using notebooks to document and run you code.
Getting set up
To get up and running using programming languages like Python and R we first need a way to write in the language and have our computers understand it. A common way to do this is to use an IDE (integrated development environment) or code editor. There are plenty of options for this but we will be using VS Code to write in Python, R Studio to write in R, and Colaboratory to create notebooks (more on that later though).
Let’s start with VS Code which can be downloaded at https://code.visualstudio.com/
VS Code is a lightweight code editor that is published by Microsoft and has a plethora of features, runs on almost any system, plus its free and open source. We wont spend too much time on downloading and setting up as Microsoft has plenty of resources that can be found at https://code.visualstudio.com/docs
Once VS Code is installed and open you should see a get started with VS Code guide that will walk you through getting set up. One thing to make sure is that you install the Python extension for VS Code. Once the walk through is complete and the Python extension installed you are ready to use VS Code for Python. You don’t necessarily need to go through all the guide and adjust all the settings just yet, take a look around and make sure you have the Python extension and you will be good to get started.

Setting up Python
For us to be able to use python first we need to install python on our computer. It is possible that Python has already been installed on your computer and you can check this by opening up your command prompt/terminal (mac: search for terminal, windows: hit the windows key and type in command, you will see the command prompt icon show up) inside the terminal/command prompt write the following and press enter/return.
python3 --versionThis will give you the version of python you have installed or return that python was not found, if you are using a recent version (3.9-3.12) you have Python and there is nothing more you need at this point. If you do not have python or have an older version, the most current stable version of Python can be found here https://www.python.org/ .

Click the button in the download menu drop down to download Python to you computer. Once downloaded you can run the installer and Python will be installed.
It should be noted that there are a multitude of way to install Python and there are different distribution with different pros and cons, for now we are just using base python.
Setting up R
Now that we have VS Code installed let’s download and install R Studio. R Studio is a IDE developed specifically for working with the R language.
R Studio can be found here https://posit.co/download/rstudio-desktop/ you will see that there are two options, one to download R, and another to download R Studio. The link to download R will take you to CRAN (comprehensive R archive network) where you can download R.
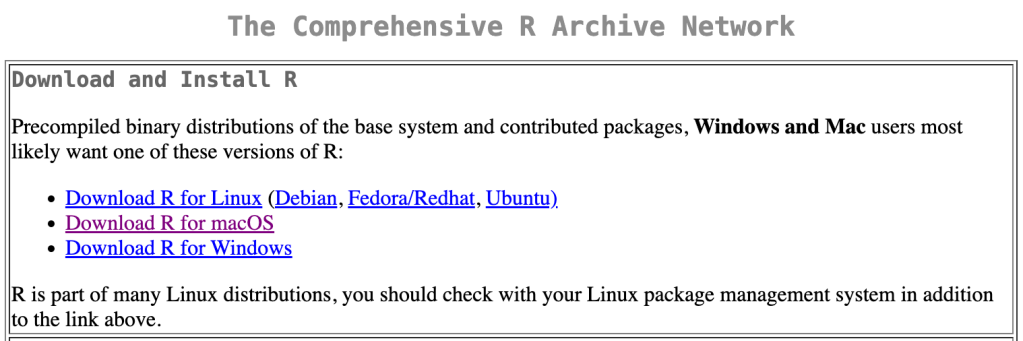
For mac users the link will take you to a page where you can choose the OS and/or chipset (eg M1/M2, Intel) that your computer has.
Once you have downloaded both files you will need to install the R language first and then proceed to install R Studio. The R installation process and R studio process is fairly straightforward and similar to installing most software. Should you have trouble manuals for different versions can be found at https://cran.r-project.org/manuals.html
Companion Repository
All of the code used in this getting started series can be found in the companion repository on Github. What’s Github you ask, it is a online repository for code, to track changes, collaborate, update, track workflows, and a host of other fun stuff. If you are serious about working with code and exploring data science, it is highly recommended to set up an account with Github. its free.
Conclusion
If you have downloaded and installed Python, R, VS Code, and R Studio you are on your way to starting a fun data science journey. In the next part of this getting started series we will explore some basics of using Python.